Plant’s pigments – building a simple chromatograph (Experiment)
Type of resource: You Tube Channel – video
Web address https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=LVsf5cEvblY
Language: Polish
Description
Experiment – constructing a simple device to investigate the pigments hidden in green and red plants. Using the results of this experiment to cook a colourful pasta (pink noodles).
Scientific concept introduced
Pigments, chromatograph, separating plants’ pigments
Creative and critical thinking
–
Mathematical reasoning
Counting
Scientific thinking
Asking questions
Predicting
Observing
Analyzing the results of chemical reaction
Drawing evidence-based conclusions
Learning how to learn
Planning the ways of using new knowledge
Additional
Hand-eye coordination
Following rules of safety and good work organization
Teamwork
Plant’s pigments – building a simple chromatograph (Experiment)
Overall aims
To introduce the concepts: plants’ pigments, chromatograph
To develop the ability to observe and record the results of observation
To develop the awareness of interconnections between plants’ pigments and the colors of the dish.
Vocabulary – keywords should be understood
Plant’s pigments, chromatograph, experiment, observation, red cabbage, czerwone vegetables (e.g.. beetroot, paprika), green vegetables (e.g.. chives, sorrel etc.), colorful pasta.
Expected learning outcomes (operational aims)
Construct a simple chromatograph following the instruction of he teacher
Draw conclusions based on collected data (count the number of divided pigments revealed on the blotter)
Record the results of observation
Cooperate in a team
Think of/offer different possibilities to use the new knowledge about the plants’ pigments
STEM skills – to which the learning unit is related to
CORE STEM SKILLS
Predicting (formulating hypothesis)
Observing
Drawing data-based conclusions
Divergent thinking
ADDITIONAL SKILLS
Teamwork
Fine motor skills
Hand-eye coordination
Teaching methodologies/activity outline
1. Problem situation – observing colors of different vegetables with the help of magnifying glass: beetroot, red cabbage, chives, red paprika, etc.
Observe the plants’ colors – how would you describe it?
How many plants are hiding in one plants? What do you think – is that 1 color or more?
2. Exploring the plants’ pigments (dividing) with the help of simple chromatograph – conducting experiment eksperymentu following the instruction on the video (teamwork – 4 teams with 4 different vegetables)
The aim: separating/ dividing the pigments in the plants
Research problem: How many different pigments are hidden in a plant? How to separate them?
Hypothesis: plants include different pigments
Ingredients/tools necessary to run the experiment by 4 teams:
– 4 vegetables in 2 different colors (red and green)
– Acetone
– Pencils
– Blotter (absorbing paper)
– Stapler
– Grinding bowl (mortar) for every team
– Spoons
Experiment
– Put the pieces of vegetable into the grinding bowl;
– Add 4 teaspoons of acetone;
– Grind the plant to the moment it turns into suspension (mixture);
– Pour the mixture into the beaker;
– Wrap one end of a long piece of blotter on the pencil and attach it with stapler
– Hang the blotter on a pencil and put the pencil on the edge of a beaker – the end of blotter should be covered in mixture into at least 1 cm;
– Leave the blotter in the mixture with acetone for 1 hour;
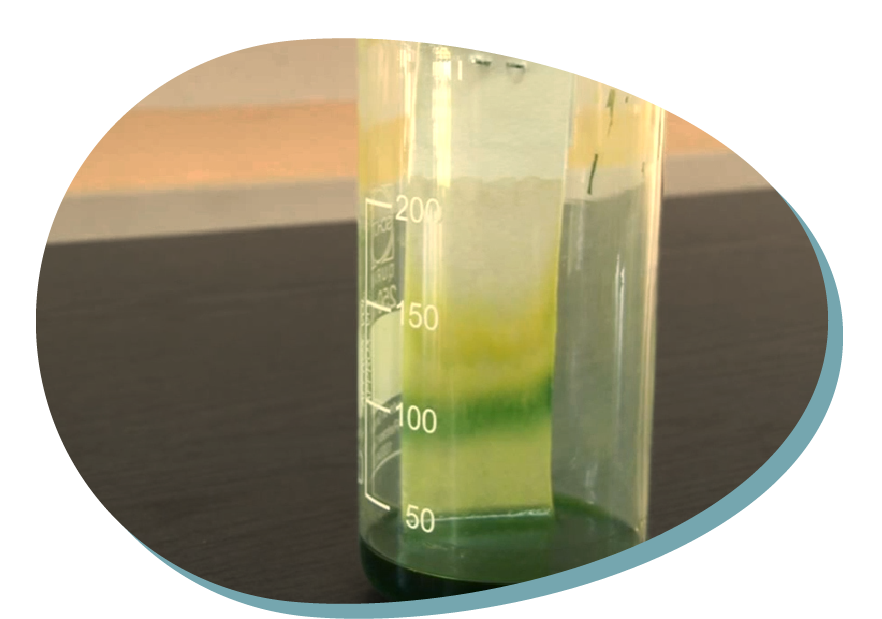
– Observe the piece of blotter – what happened?
3. Drawing conclusions from observation:
What have you observed on the blotter?
What have we learned about plants’ pigments
How many different colors/ pigments can you observe? How many pigments are hiding in the plant you were exploring?
What kind of name can we give to the device we have constructed? Let the children think about their own name, and then explain that the device is called “chromatograph”
Conclusion
On the blotter one can observe several strips of different colors. The device we constructed is called “chromatograph” and revealed the fact that plants’ pigments are complex and they can disassembled.
4. Recording the results of the observation – planning the possibilities to use the new knowledge:
Try to record what you have observed – in the form of drawing.
How can we use the knowledge about plants’ pigments? What can do with it?
5. Using the results of observation to cook the magical color changing pasta – following the instruction on the video: https://leftbraincraftbrain.com/magical-color-changing-unicorn-noodles/
Assessment of learning
Children self-assessment – What have I learned today? What else would I like to know? What was the most difficult to do? What was the most surprising to find out?
Equipment and materials to be used in learning unit (tools, ingredients etc)
– 4 plants/ vegetables of different colors (red paprika, beetroot, chives, sorrel etc.)
– Magnifying glass for every team
– Beaker for every team
– Acetone
– Pencils
– Blotter (absorbing paper)
– Stapler
– Grinding bowl (mortar) for every team
– Worksheets for noting observation results
– Large pot for boiling water
– Leaves of red cabbage
– Pasta
– Salt
– Lemon
– Small electric cooker for boiling pasta in the classroom or access to preschool kitchen
Kind of setting
Preschool classroom and kitchen (ot a small electric device for cooking in the classroom)
References – source
PCEN Rzeszów. Erasmus+ Project: Through the world with mathematics. In search of new methods for teaching maths and similar subjects. You Tube Channel https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=LVsf5cEvblY
Magical Color Changing Unicorn Noodles: https://leftbraincraftbrain.com/magical-color-changing-unicorn-noodles/
Plant’s pigments – building a simple chromatograph (Experiment)
1. Usefulness for STEM education – integrating content of different disciplines
Cross-curricular character of the resource

The range of S-T-E-M subjects included

The presentation of possibilities of including artistic activities (STEAM approach)

2. Expected learning outcomes
Consistency (links) with preschool core curriculum

Communicativeness of description

3. Methodology of teaching
Clarity, communicativeness of instructions for teachers

Meaningful learning – using practical life problems

Original idea

The level of ease in implementing the methodology to preschool age children

The level of ease in preparing necessary ingredients, materials and equipment needed

4. Sustainability
Ecological characteristics of materials/ results

Supporting healthy eating habits

Low ecological footprint

Possibilities of inclusion (respecting cultural diversity and food intolerances)

5. Class management
Using differentiated forms of work – individual, team work etc.

Individual work

Team work

Whole group
6. Time management

Short activity (10-15 minutes)

Medium activity (20-30 minutes)

Long activity (1 hour or more)

Very long activity (1 day or more)
PDF: https://www.printfriendly.com/p/g/qJYUxM